- 2020-11-04
- 0.0 Reitingas
- 556 Peržiūrų
- Aptarti
The virus that causes COVID-19 was present in New York City long before the city's first case of the disease was confirmed on March 1, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai report. Their study found that more than 1.7 million New Yorkers—about 20 percent of the city's population—have already been infected with the virus, known as SARS-CoV-2, and that the infection fatality rate of the virus is close to 1 percent, ten times deadlier than the flu.
Results of the retrospective surveillance study of more than 10,000 plasma samples taken from the beginning of February to July will be published in Nature on Tuesday, November 3.
A sharp rise in infections in New York City occurred in the week ending March 8, followed by a significant increase of COVID-19 deaths during the week ending March 15. New York State implemented a stay-at-home order March 22, after which daily case numbers in New York City started to plateau and then decreased in April and May.
Very little testing capacity was available at the beginning of the local epidemic in early March, but, "We now know there were many asymptomatic and mild to moderate cases that likely went undetected," said Emilia Mia Sordillo, MD, Ph.D., Associate Professor of Pathology, Molecular and Cell Based Medicine, Director of Clinical Microbiology, an attending physician in Infectious Diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine and the Mount Sinai Health System, and a senior author on the paper. "In this study, we aimed to understand the dynamics of infection in the general population and in people seeking urgent care."
The study findings are based on a dataset of 10,691 plasma samples from Mount Sinai Health System patients obtained and tested between the weeks ending February 9 and July 5. The first group included 4,101 samples from patients seen in Mount Sinai's emergency departments and from patients that were admitted to the hospital for urgent care. This group, termed the "urgent care" group, served as a positive control group designed to detect increasing SARS-CoV-2 infections in individuals with moderate to severe COVID-19 as the local epidemic progressed. The second group of 6,590 samples, termed the "routine care" group, were obtained from patients at OB/GYN visits, labor and deliveries, oncology-related visits, hospitalizations due to elective surgeries and transplant surgeries, preoperative medical assessments and related outpatient visits, cardiology office visits, and other regular office/treatment visits. Researchers reasoned that these samples might resemble the general population more closely because the purposes for these scheduled visits were unrelated to acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. The urgent care group comprised 45.5 percent females while the routine care group included 67.6 percent females. The majority of individuals in the urgent care group were over 61 years of age while the routine care group had a more balanced age distribution that more closely resembled the general population adult population.
To estimate true infection rates, researchers measured the presence of antibodies to past SARS-CoV-2 infections, rather than the presence of the virus, in weekly intervals. The antibody test used in this research—an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)— was developed and launched at Mount Sinai and is able to detect the presence or absence of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, as well as the titer (level) of antibodies an individual has. The high sensitivity and specificity of this test—meaning that the rate of false negatives and false positives is low—allowed it to be among the first to receive emergency use authorization from New York State and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
"Our two-step ELISA test confirms the presence and level antibodies. The use of two sequential tests reduces the false positive rate and favors high specificity resulting in a sensitivity of 95 percent and a specificity of 100 percent," said Viviana Simon, MD, Ph.D., Professor of Microbiology, and Medicine; a member of the faculty of the Global Health and Emerging Pathogens Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine; and a senior author on the paper.
Seroprevalence increased at different rates in both groups, rising sharply in the urgent care group. Notably, seropositive samples were found as early as mid-February (several weeks before the first official cases) and leveled out at slightly above 20 percent in both groups after the epidemic wave subsided by the end of May. From May to July, seroprevalence and antibody titers stayed stable, suggesting lasting antibody levels in the population.
"Our data suggests that antibody titers are stable over time, that the seroprevalence in the city is around 22 percent, that at least 1.7 million New Yorkers have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 so far, and that the infection fatality rate is 0.97 percent after the first epidemic wave in New York City," said Florian Krammer, Ph.D., Mount Sinai Professor in Vaccinology at the Icahn School of Medicine and corresponding author on the paper. "We show that the infection rate was relatively high during the first wave in New York but is far from seroprevalence that might indicate community immunity (herd immunity). Knowing the detailed dynamics of the seroprevalence shown in this study is important for modeling seroprevalence elsewhere in the country."
- by The Mount Sinai Hospital
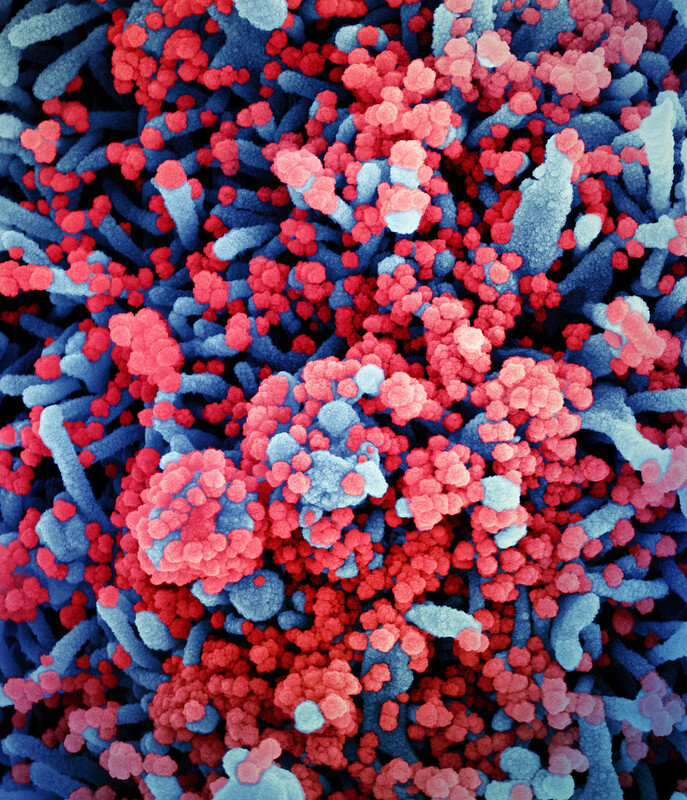
- Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a cell (blue) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (red), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID
...kadangi jau perskaitėte šį straipsnį iki pabaigos, prašome Jus prisidėti prie šio darbo. Skaitykite „Paranormal.lt“ ir toliau, skirdami kad ir nedidelę paramos sumą. Paremti galite Paypal arba SMS. Kaip tai padaryti? Iš anksto dėkojame už paramą! Nepamirškite pasidalinti patikusiais tekstais su savo draugais ir pažįstamais.
Turite savo nuomone, tapk autoriumi, prisijunk ir rašykite bloge. Dalinkitės receptais, sveikatos patarimais, nutikimais, susidūrėte su nekasdieniškais reiškiniais. Galite išversti iš užsienio kalbos, talpinkite su nuoroda. Laukiame Jūsų straipsnių, naujienų, apžvalgų ar istorijų!
Susijusios naujienos
Būkite pirmi, kurie pasidalins savo nuomonėmis su kitais.
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
