- 2020-10-20
- 0.0 Reitingas
- 561 Peržiūr
- Aptarti
In a major breakthrough an international team of scientists, led by the University of Bristol, has potentially identified what makes SARS-CoV-2 highly infectious and able to spread rapidly in human cells. The findings, published in Science today [20 October] describe how the virus's ability to infect human cells can be reduced by inhibitors that block a newly discovered interaction between virus and host, demonstrating a potential anti-viral treatment.
Unlike other coronavirus, which cause common colds and mild respiratory symptoms, SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, is highly infective and transmissive. Until now, major questions have remained unanswered as to why SARS-CoV-2 readily infects organs outside of the respiratory system, such as the brain and heart.
To infect humans, SARS-CoV-2 must first attach to the surface of human cells that line the respiratory or intestinal tracts. Once attached, the virus invades the cell then replicates multiple copies of itself. The replicated viruses are then released leading to the transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
The virus's process of attachment to and invasion of human cells is performed by a viral protein, called the 'Spike' protein. Understanding the process by which the 'Spike' protein recognises human cells is central to the development of antiviral therapies and vaccines to treat COVID-19.
In this breakthrough study, the research groups in Bristol's Faculty of Life Sciences, Professor Peter Cullen from the School of Biochemistry; Dr. Yohei Yamauchi, Associate Professor and virologist from the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, and Dr. Boris Simonetti, a senior researcher in the Cullen lab, used multiple approaches to discover that SARS-CoV-2 recognises a protein called neuropilin-1 on the surface of human cells to facilitate viral infection.
Yohei, Boris and Pete explained: "In looking at the sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein we were struck by the presence of a small sequence of amino acids that appeared to mimic a protein sequence found in human proteins which interact with neuropilin-1. This led us to propose a simple hypothesis: could the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 associate with neuropilin-1 to aid viral infection of human cells? Excitingly, in applying a range of structural and biochemical approaches we have been able to establish that the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 does indeed bind to neuropilin-1.
"Once we had established that the Spike protein bound to neuropilin-1 we were able to show that the interaction serves to enhance SARS-CoV-2 invasion of human cells grown in cell culture. Importantly, by using monoclonal antibodies—lab-created proteins that resemble naturally occurring antibodies—or a selective drug that blocks the interaction we have been able to reduce SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect human cells. This serves to highlight the potential therapeutic value of our discovery in the fight against COVID-19."
Intriguingly, scientists at the Technical University of Munich, Germany and the University of Helsinki, Finland, have independently found that neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity.
Together the Bristol researchers concluded: "To defeat COVID-19 we will be relying on an effective vaccine and an arsenal of anti-viral therapeutics. Our discovery of the binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike to neuropilin-1 and its importance for viral infectivity provides a previously unrecognised avenue for anti-viral therapies to curb the current COVID-19 pandemic."
- by University of Bristol
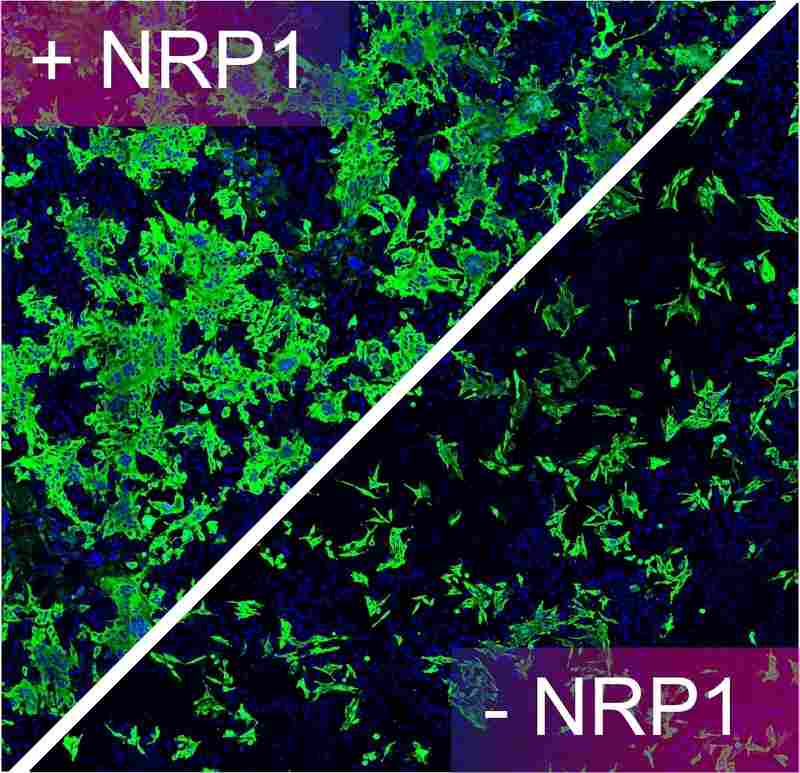
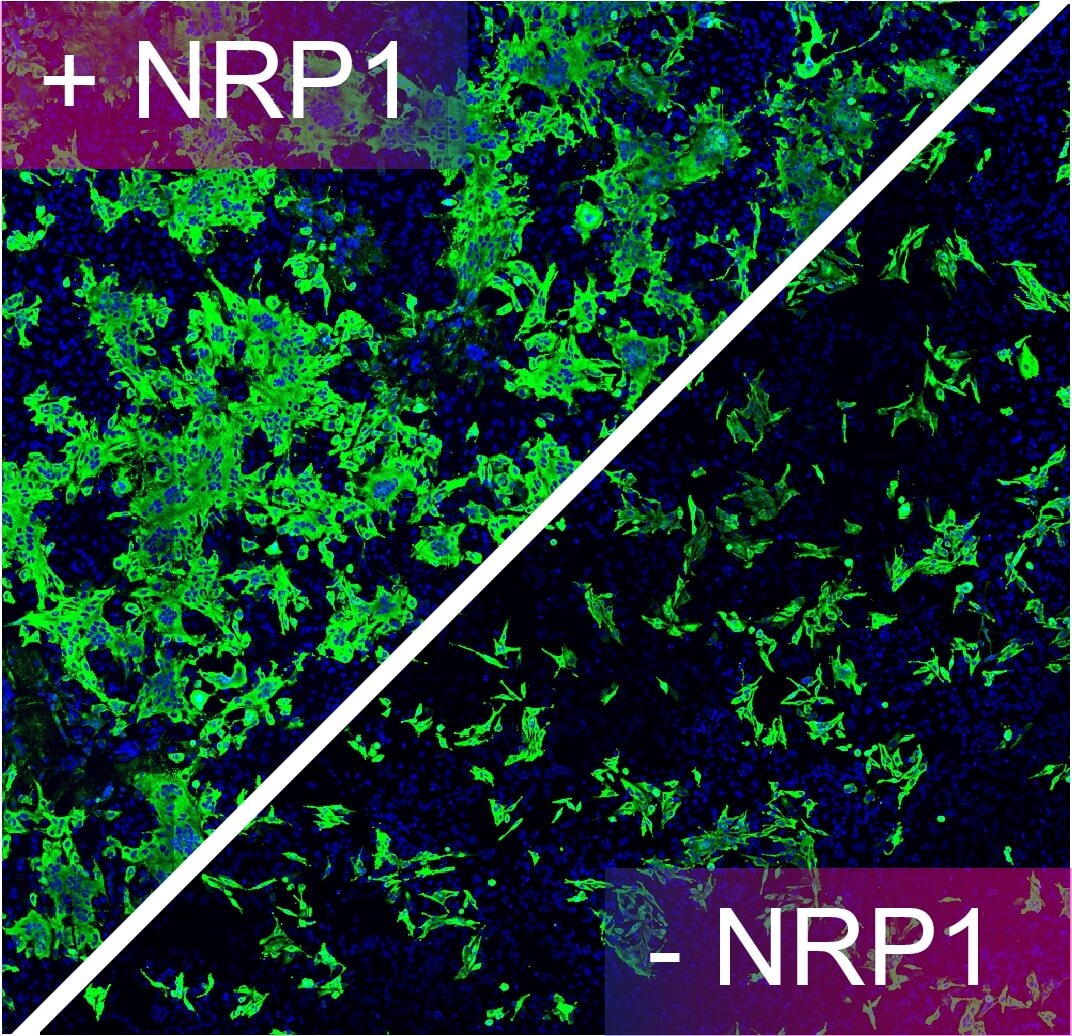
- Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection. This is an image of human cells incubated with SARS-CoV-2, infected cells are labelled green. Removal of NRP1 drastically reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection in human cell cultures. Reduction of infection can also be observed when cells were treated with a drug or an antibody targeting NRP1. Credit: The University of Bristol
...kadangi jau perskaitėte šį straipsnį iki pabaigos, prašome Jus prisidėti prie šio darbo. Skaitykite „Paranormal.lt“ ir toliau, skirdami kad ir nedidelę paramos sumą. Paremti galite Paypal arba SMS. Kaip tai padaryti? Iš anksto dėkojame už paramą! Nepamirškite pasidalinti patikusiais tekstais su savo draugais ir pažįstamais.
Turite savo nuomone, tapk autoriumi, prisijunk ir rašykite bloge. Dalinkitės receptais, sveikatos patarimais, nutikimais, susidūrėte su nekasdieniškais reiškiniais. Galite išversti iš užsienio kalbos, talpinkite su nuoroda. Laukiame Jūsų straipsnių, naujienų, apžvalgų ar istorijų!
Susijusios naujienos
Būkite pirmi, kurie pasidalins savo nuomonėmis su kitais.
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau
Skaityti daugiau